Welcome To CB Piping System Co., ltd., ...
What are the Advantages of Industrial Biomass Hot Air Furnaces?
Release time:
2025-08-11
Industrial biomass hot air furnaces have notable advantages in energy efficiency, environmental protection and economy, with wide applications. Despite limitations, they have bright prospects.
Industrial biomass hot air furnaces offer numerous advantages, spanning energy efficiency, environmental protection, and economic benefits. As a key industrial energy conversion device, biomass hot air furnaces have garnered widespread attention in recent years, especially against the backdrop of promoting renewable energy and environmental protection (Lu et al., 2024)[1].
Energy Efficiency and Fuel Characteristics
Biomass fuels themselves have inherent advantages. Compared to traditional fuels, biomass fuels come from diverse sources, including agricultural and forestry waste, energy crops, and more (Đurović et al., 2016)[2] (Amalina et al., 2023)[3]. The carbon dioxide emitted during biomass combustion is roughly equivalent to the amount absorbed by plants during growth, contributing to carbon neutrality (Hong, 2024)[4]. Additionally, biomass fuels are generally priced relatively low, which can effectively reduce energy costs (Ren et al., 2019)[5] (Bikár et al., 2018)[6]. For example, when biomass pellet fuel (with a calorific value of 3,550 kcal/kg) is used in automated tobacco curing furnaces, 1.2 kg of biomass pellets are required per kg of dry tobacco leaves (Ren et al., 2019)[5].
Technical Advantages of the Hot Air Furnace System
The design of biomass hot air furnaces is becoming increasingly advanced. New industrial biomass hot air furnace systems, through innovative designs, have effectively addressed issues such as incomplete combustion and coking in traditional biomass boilers (Lu et al., 2024)[1]. By optimizing air supply, the combustion of biodiesel in industrial furnaces can achieve energy conservation and emission reduction (Jiang et al., 2024)[7]. Furthermore, combined with high-temperature air combustion technology, biomass hot air furnace systems can achieve higher thermal efficiency, reduce nitrogen oxide emissions, and lower excess air coefficients, thereby enabling equipment miniaturization (Wang et al., 2006)[8]. Some studies have shown that when the oxygen concentration in excess air is reduced from 4% to 3%, furnace efficiency can increase by 0.6% (Lee & Jou, 2011)[9].
Environmental Benefits
The use of biomass hot air furnaces significantly reduces environmental pollution. Biomass combustion produces fewer harmful gases such as sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides, resulting in relatively little impact on the environment (Wang et al., 2006)[8] (Hong, 2024)[4]. Especially in scenarios where traditional coal-fired boilers are replaced, biomass boilers can significantly reduce harmful substance emissions and improve air quality (Marganingrum et al., 2022)[10].
Economic Benefits and Policy Support
Beyond environmental benefits, biomass hot air furnaces also offer favorable economic returns. Although the initial investment may be higher, long-term operating costs are relatively low, especially when biomass fuel prices are stable (Ren et al., 2019)[5] (Bikár et al., 2018)[6]. More importantly, many regions have introduced policies to support the development and application of biomass energy, providing certain financial subsidies and tax incentives, which further reduce the application costs of biomass hot air furnaces (Qv et al., 2021)[11].
Application Scenarios
Biomass hot air furnaces have a wide range of applications. For instance, they can be used in agricultural and industrial processes such as wood drying and grain dehydration (Lu et al., 2024)[1] (Qu et al., 2021)[12]. In building heating, biomass boilers are gradually being adopted, especially in multi-family residences to replace traditional fossil fuel boilers, achieving significant energy-saving and emission-reduction effects (Las-Heras-Casas et al., 2018)[13]. Additionally, combined with other renewable energy sources like solar energy, biomass hot air furnaces can form multi-generation systems, providing users with electricity, heat, cooling, and other energy services (Liu et al., 2024)[14] (Zhang et al., 2018)[15].
Limitations and Challenges
Despite their many advantages, biomass hot air furnaces have some limitations. For example, biomass fuels have relatively low energy density and require large storage spaces (Zhang et al., 2018)[16]. Moreover, biomass pretreatment (such as drying and crushing) consumes a certain amount of energy. The combustion efficiency and emission levels of biomass hot air furnaces are also limited by fuel quality and combustion technology, requiring continuous improvement and optimization (Lu et al., 2024)[1].
Future Development Directions
The future development of biomass hot air furnaces will focus on the following aspects:
Improving combustion efficiency: Achieving full combustion of biomass fuels and enhancing thermal efficiency through improved combustion technologies and optimized furnace structures (Kilinç et al., 2014)[17] (Jin et al., 2020)[18].
Reducing emissions: Adopting advanced flue gas purification technologies to reduce emissions of particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and other pollutants, meeting increasingly stringent environmental requirements (Dong & Wang, 2019)[19].
Expanding fuel sources: Developing diversified biomass fuels, including agricultural and forestry waste, energy crops, and urban organic waste, to realize the sustainable utilization of biomass resources (Castro et al., 2023)[20] (Amalina et al., 2023)[3].
Intelligent control: Applying advanced control systems to achieve automated operation and intelligent management of biomass hot air furnaces, improving operational efficiency and safety.
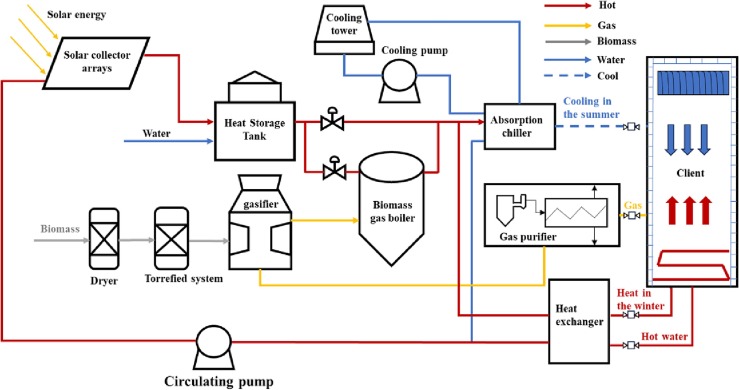
Combined Energy System
Source: (Liu et al., 2024)[14]
The combined biomass and solar energy system can provide users with sustainable energy supply.
In summary, industrial biomass hot air furnaces have significant advantages in energy, environmental, and economic aspects, making them an important pathway to achieve sustainable development in the industrial sector. Through continuous technological innovation and policy support, biomass hot air furnaces will play a greater role in the future.
Author: Hangzhou Thermal Engineering Technology Co., Ltd.
Source: Journal and Conference Papers